Abstract
Background: Race/ethnicity and socioeconomic status (SES) have been associated with access to and outcomes after hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT). The role of health disparity factors beyond race/SES in HCT outcomes, however, has not been well described. This is especially true for long-term HCT survivors, for whom local socio-demographic factors may have a greater impact on outcomes because patients may no longer be under close monitoring of their transplant center. The County Health Rankings and Roadmaps (CHRR) provides updated aggregated information from several publicly available datasets to comprehensively describe the health status of US counties. A recent report demonstrated an association between community health status and 1-year non-relapse mortality in a CIBMTR cohort of allogeneic HCT recipients (Hong et al., Cancer 2021). We conducted a single-center retrospective cohort study to investigate the association between community health and long-term outcomes in 1-year autologous and allogeneic HCT survivors.
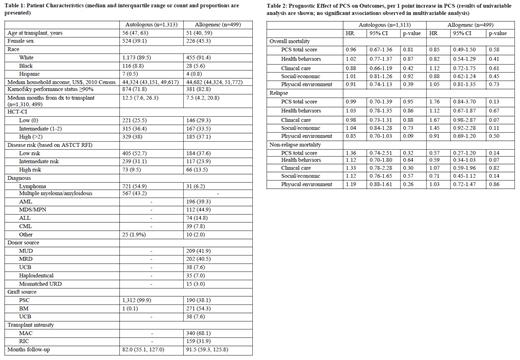
Methods: Our study included 1,812 consecutive adult patients from Cleveland Clinic's BMT Program database who received their first allogeneic or autologous HCT between 2003 and 2017 and survived at least 1 year after their transplant. We used patient community risk score (PCS) as the surrogate for community health. PCS was nationally standardized and calculated as the sum of weighted Z-scores of the 23 county-level community health factors considered in CHRR. The 23 factors fell under 4 categories of health factors: health behavior (tobacco and alcohol use, etc.), clinical care (access and quality of care), social and economic factors (education, community safety, etc.), and physical environment (environmental quality and built environment). Higher PCS indicate worse community health. We evaluated the association of PCS with overall survival (OS), relapse, and non-relapse mortality (NRM) with Cox or Fine and Gray regression separately for autologous and allogeneic HCTs. Considered co-variables included pre-transplant sociodemographic data, disease diagnosis, and transplant factors.
Results: Autologous HCT recipients (n=1,313) lived in 133 of 3,141 CHRR counties, 90% in Ohio. Similarly, allogeneic recipients (n=499) were from 88 counties, 88% in Ohio. Patient characteristics are shown in Table 1. The median (range) PCS scores for autologous and allogeneic HCT recipients were 0.03 (-0.85, 0.97) and 0.03 (-0.85, 0.58), respectively. For comparison, the PCS for the complete US CHRR dataset ranged from -1.43 to 2.54 and ranged from -1.6 to 2.0 in the prior CIBMTR study that included allogeneic HCT recipients (Hong et al., Cancer 2021). PCS was not associated with OS, relapse, or NRM for autologous or allogeneic HCT recipients in univariable analysis, nor were the four categories of health factors that contribute to the total PCS (Table 2). In addition, race and estimated median household income were not associated with mortality. Similar findings were noted in multivariable analysis.
Conclusion: In our single center study, PCS was not associated with OS, relapse, or NRM in allogeneic or autologous HCT recipients who survived at least 1 year after HCT. A limitation of our analysis is that our cohort represented a single center with regional representation, where long-term follow up care is provided through a dedicated survivorship clinic and there is a strong emphasis on psychosocial support. A national cohort with greater geographical diversity is needed to better define the association of community factors and outcomes in long-term HCT survivors.
Hamilton: Syndax: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Equilium: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Majhail: Anthem, Inc: Consultancy; Incyte Corporation: Consultancy.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal